The demand for eLearning localization has never been higher than it is today.
Trainers, instructors, and teachers are increasingly facing a common headache – how to localize content effectively.
It’s not just about translating words; it’s about making every lesson resonate across diverse cultures and languages.
This challenge is daunting, yet, with the right process and strategies, it’s entirely achievable.
Join me as we dive into the world of the eLearning localization process and strategies to explore how to overcome this pain point.
What Is eLearning Localization?
eLearning localization is the process of adapting digital learning materials for learners in a specific geographical region or cultural group.
This goes beyond mere translation of text and encompasses the adaptation of elements such as images, symbols, currencies, examples, number formats, and cultural references. It is intended to ensure that the eLearning content is relevant, understandable, and culturally appropriate for the target audience.
With localization, you can provide an immersive and engaging learning experience that feels tailor-made for learners, regardless of their cultural or linguistic background.
Importance of eLearning Localization
The significance of localization of eLearning can be distilled into several key points:
1. Breaking Language Barriers
90% of people prefer to learn in their native language.
Localization dismantles language barriers and makes education more accessible to a global audience. This inclusivity not only broadens the reach of eLearning materials but also opens up educational opportunities to non-English speakers.
2. Cultural Sensitivity
By adapting content to meet cultural norms and expectations, localization ensures that eLearning is respectful and sensitive to the cultural values of its audience. This fosters a positive learning environment and reduces the risk of cultural misunderstandings.
3. Market Expansion
For eLearning providers, localization presents an opportunity to enter new markets and attract a diverse learner base. This expansion can lead to increased enrollment rates and revenue growth.
4. Learner Engagement
Localization adjusts the content to fit the cultural context and language of the learners. This makes it more relatable and engaging, besides increasing the likelihood of learners completing the course and retaining the information.
5. Increased Course Effectiveness
Localized content is more likely to resonate with learners, as it considers their cultural norms and values. This leads to a deeper understanding and more effective learning outcomes.
6. Greater Compliance
Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements or cultural sensitivities. Localization helps ensure that eLearning content complies with local laws and norms, reducing the risk of offending learners or facing legal issues.
eLearning Localization Process With Example
Here’s a detailed look at how the process of localization works in eLearning, followed by a relatable example.
1. Analysis & Cultural Adaptation
The process starts with identifying the target audience.
Understand their language, cultural norms, learning styles, and any regional regulations that might affect content delivery.
Adapt content to reflect local customs, values, and etiquette. This may involve changing examples, idioms, and cultural references to make them more relatable.
2. Localization of Content
Translating text from the source language to the target language(s) is another key step. It ensures that the translation is accurate and culturally appropriate.
You should adapt visual elements, such as images and videos, to reflect the cultural context of the target audience. This could include changing colors, symbols, or gestures that may carry different meanings in different cultures.
Similarly, for audio and video content, provide dubbed voice-over or subtitles in the target language(s).
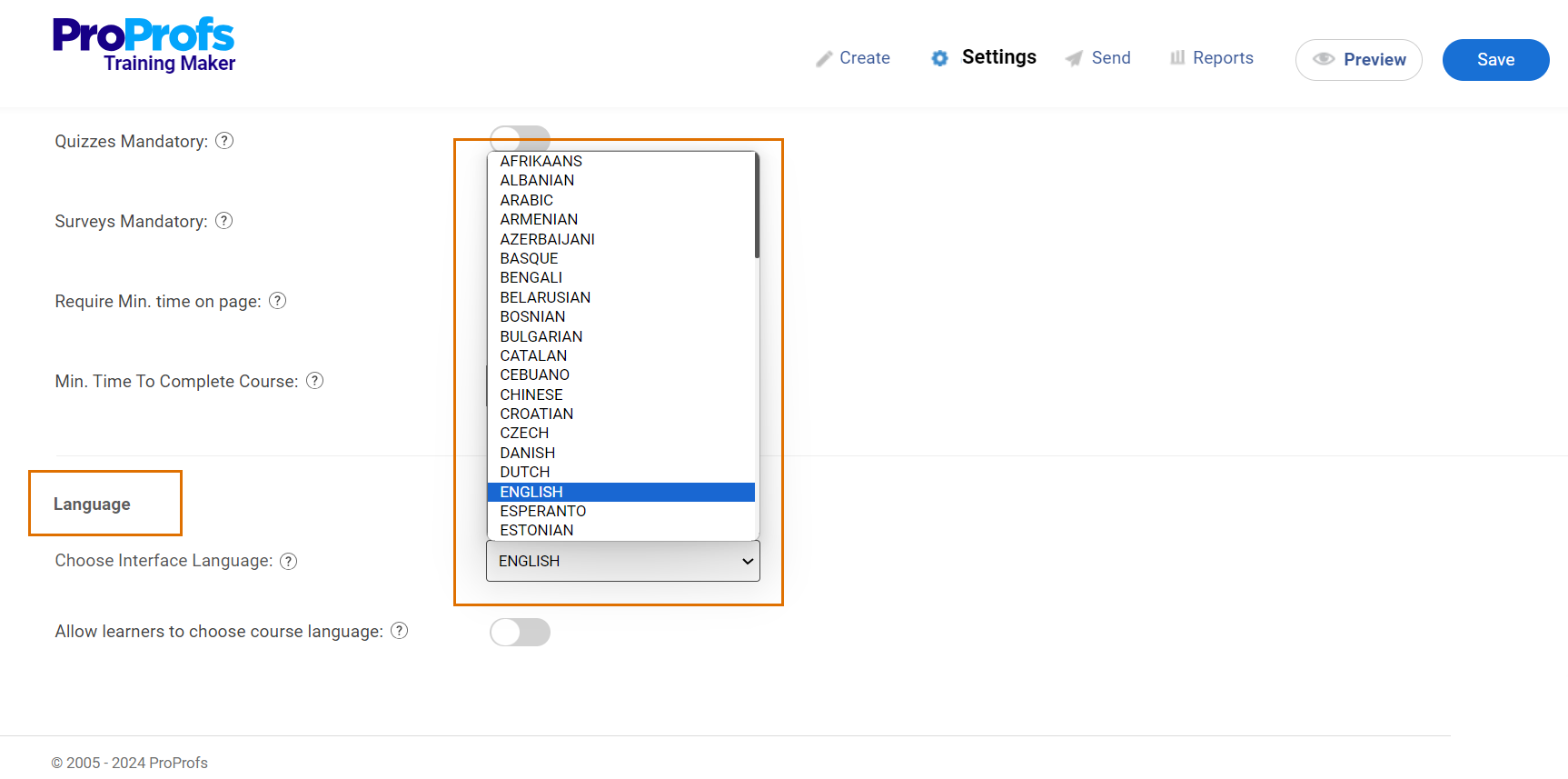
Here’s how you can change the language of your course by using a robust cloud LMS, such as ProProfs Training Maker.
3. Technical Adaptation
Adaptation to local technologies ensures that the content is compatible with local internet speeds, devices, and software preferences.
You should adapt the layout for languages like Arabic and Hebrew to accommodate right-to-left reading.
4. Legal Requirements & Compliance
Adapt your content to meet local regulations on accessibility standards for learners with disabilities.
Also, ensure the eLearning content complies with local data protection laws like GDPR in Europe.

5. Testing & Quality Assurance
Linguistic testing is about ensuring the translation is accurate, and the language flows naturally.
Likewise, functional testing ensures all components of the eLearning course work as expected in the localized version.
Finally, gather feedback from a sample of your target audience to conduct usability testing that shows that the localized content meets their needs and expectations.
6. Launch and Feedback Collection
This phase is crucial for the long-term success and continuous improvement of the localized eLearning content.
After thorough testing, launch the localized eLearning content. The launch should be planned strategically. This might include a phased rollout to different regions or segments of the target audience.
Soon after that, you can collect feedback from users and stakeholders to know what works and what doesn’t as well as identify any areas for improvement. Based on that, you can make the necessary adjustments.
Example: Localizing a Business Course for Japan

Imagine an eLearning platform based in the United States offering a course on business communication skills in English. To localize this course for a Japanese audience, the process might involve:
- Understanding Japanese business etiquette and communication styles, which are more formal and indirect compared to American styles.
- Translating the course material into Japanese, including text, voice-overs, and subtitles. Adapting examples to reflect Japanese business contexts, like the importance of business cards (meishi) and bowing.
- Ensuring the course is compatible with commonly used devices and internet speeds in Japan. Adapting the layout for any Japanese text that might require vertical writing.
- Adapting the course to comply with Japanese data protection laws, such as the Act on the Protection of Personal Information (APPI).
- Conducting linguistic, functional, and usability testing with a Japanese audience to ensure the course meets their needs and expectations.
- Launching the localized course in Japan and collecting feedback for continuous improvement.
This example underscores the comprehensive approach required for eLearning localization to ensure the content is not only translated but also fully adapted to meet the needs and expectations of the target audience.
Strategies for Effective eLearning Localization
The following is a list of tried and tested best practices I’ve seen and utilized in the online learning and training space for making eLearning localization impactful in the long run.
1. Understand Cultural Nuances
Localization must account for cultural sensitivities, idiomatic expressions, and social norms. This involves adapting examples, metaphors, and case studies to be culturally relevant and respectful.
For example, a global fast-food chain’s eLearning module for employees included references to cricket when discussing teamwork in the Indian version. For its U.S. counterpart, these references were changed to football, given its popularity in that country, ensuring cultural relevance.
2. Incorporate Local Laws & Regulations
This is another vital eLearning localization strategy.
Legal requirements vary greatly across regions. eLearning courses should be localized to comply with local laws, especially for subjects like compliance, safety, and employment.
Image source: ProProfs
Here’s what it looks like. If you’re an international pharmaceutical company, you may be required to localize your compliance training for each country to adhere to local pharmaceutical regulations and practices.
Remember: Consult local legal experts to ensure your content meets all legal requirements in the target region.
3. Adapt to Local Learning Styles
Educational norms and learning styles differ around the world. Some cultures prefer hierarchical, instructor-led sessions, while others value collaborative and interactive learning.
For example, in adapting an eLearning course for South Korea, you should transition from a purely self-led model to include more structured, instructor-led components, aligning with the local preference for hierarchical educational structures.
Research and integrate local educational practices and preferences to enhance learner engagement.
4. Optimize for Local Technology & Infrastructure
Internet speeds, device usage, and technological infrastructure vary globally. eLearning content should be accessible and functional across the spectrum of technological environments.
A good case in point is an NGO that optimizes its eLearning platform for mobile access with low bandwidth requirements in African countries. This indicates the recognition of the prevalent use of mobile devices and varying internet speeds.
Along with this, you should acknowledge the key role AI plays today in the localization of eLearning. The technology enhances the learning experience through natural language processing and machine learning algorithms, which help tailor the content to the learners’ linguistic and cultural contexts.
As Shannon Zimmerman, CRO at Summa Linguae Technologies, said, “AI in localization can be a real game changer and transformational compared to historical approaches.”
5. Engage with Local Experts & Educators
Collaboration with local subject-matter experts and educators can lead to the accuracy, relevancy, and effectiveness of your content. They can provide insights into local nuances that might not be obvious to outsiders.
For example, a multinational corporation developing a management training program in Brazil may collaborate with Brazilian management experts who specialize in areas like business strategy, organizational behavior, human resources, financial management, and operations management. This will enable the corporation to embrace local business practices and leadership styles.
What You Can Do: Establish a review panel of local experts for content validation and cultural appropriateness.
6. Use Local Voices for Audiovisual Content
Voiceovers and videos should use local accents and dialects to ensure relatability and comprehension. This will enhance the learner’s connection with the material.
If you’re developing an eLearning course on customer service skills, consider using voice actors with a variety of British accents for your UK version. This will mirror the diversity of the local population.
Select voice talent who not only speaks the language but also embodies the local accent and intonations accurately.
7. Iterative Testing & Feedback Loops
Continuous testing with local learners provides insights into usability, engagement, and comprehension. Feedback loops make room for ongoing adjustments and improvements.
For example, a software company developing eLearning modules for its product continuously tested its courses in different markets by using feedback to tweak content and presentation style.
Each of these strategies emphasizes the importance of a nuanced, culturally sensitive approach to eLearning localization. This will help you ensure that your content is understood and it resonates with the intended audience.
Get Free eLearning Authoring Software — All Features, Forever.
We've helped 567 companies train 200,000+ employees. Create courses in under a minute with our AI LMS or use 200+ ready-made courses on compliance, harassment, DEI, onboarding, and more!
Get Your eLearning Localization Process Rolling!
It’s clear that the task of eLearning localization is both an art and a science. From understanding cultural nuances to adapting to local learning styles and complying with area-specific laws, the process demands a multifaceted approach.
But the rewards—engaging and educating learners across the globe—are immense. I’ve outlined effective strategies, from embracing localization at the design phase to choosing the right tools and partners.
A tool like ProProfs Training Maker can be your reliable ally with its excellent customization features like time, language, and other settings to cater to specific audiences in selected locations.
The path forward may seem complex, but it’s paved with opportunities for those ready to embrace it. Now is the time to take the next step and expand your reach and impact.
Don’t just cross borders; erase them. Create learning experiences that are truly universal!
 Tips
Tips
We’d love to hear your tips & suggestions on this article!
Get Free eLearning Authoring Software — All Features, Forever.
We've helped 567 companies train 200,000+ employees. Create courses in under a minute with our AI LMS or use 200+ ready-made courses on compliance, harassment, DEI, onboarding, and more!

 We'd love your feedback!
We'd love your feedback! Thanks for your feedback!
Thanks for your feedback!







